
EPA Is Right To Defend the Lead and Copper Rule Improvements

EPIC Comments on Texas Draft SFY 2026 Drinking Water State Revolving Fund (DWSRF) Lead Service Line Replacement (LSLR) Program
Understanding State-by-State Differences in IUPs and Project Lists: Findings from EPIC’s DWSRF Funding Tracker

Differences in How States Organize Their Intended Use Plans (IUPs) and Project Lists

New Policy Resources for Addressing Climate Adaptation Funding Barriers Experienced by Northwest Coastal Tribes

Why NJ's Permitting Play Matters: A Closer Look at Governor Sherrill's Executive Order on Permitting

2025 In Review: Technology

2025 In Review: Agriculture
How IIJA Lead Replacement Funding Is Moving: New State Profiles from EPIC

EPIC's Written Testimony for January 2026 EPW Hearing on Federal Environmental Review and Permitting Processes

EPIC Comments on Texas' $1B Water Supply and Infrastructure Grant Implementation Plan

There are Nine Types of Permitting Reform

30 Permitting Wins in 30 Days
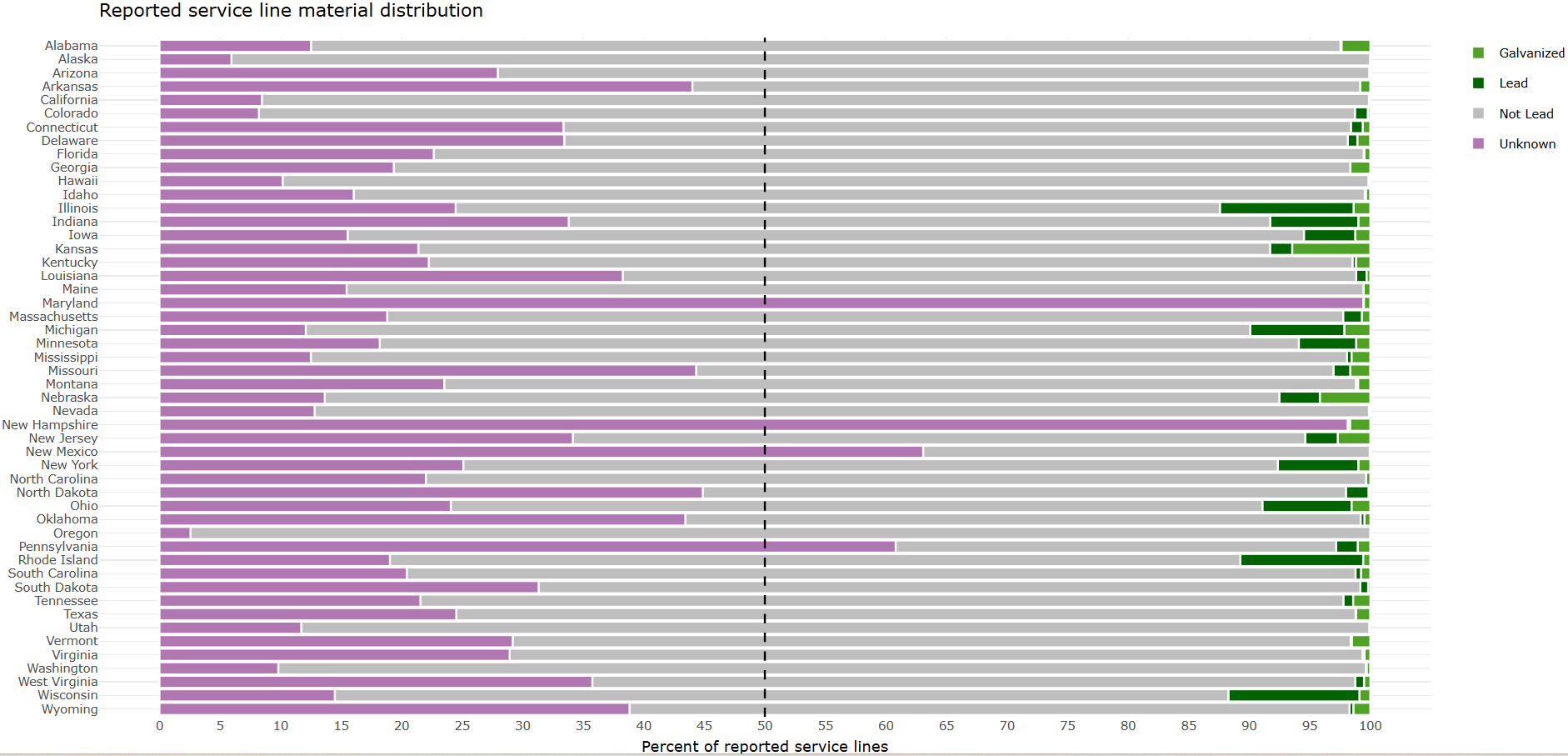
What Best Available Data Tells Us About Lead Service Lines

EPIC Partners with National Academy of Public Administration to Accelerate Climate Resilience

2025 Lead Pipe Funding: The Good, the Bad, and the Big Opportunities Ahead

EPIC DWSRF Funding Tracker: Texas

EPIC DWSRF Funding Tracker: Mississippi

Tech Capacity in Transition: Barriers and Opportunities in Tech Talent


